 AMR Sensor
AMR Sensor
Technical document: The principle of operation of the AMR sensor is explained.
Represents the equivalent circuit of an AMR sensor. The resistor pattern indicates the direction of extension of the element on the magnetic sensing surface.
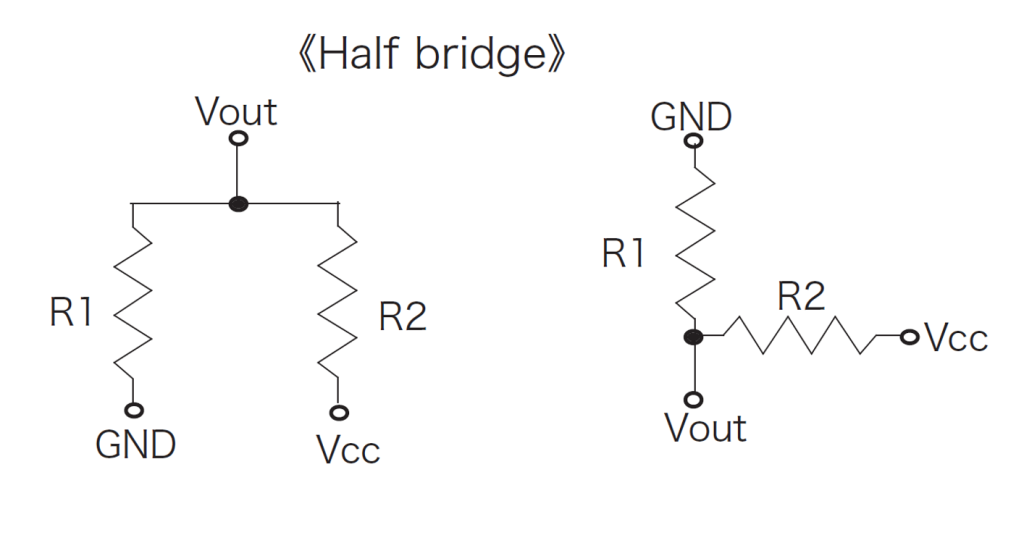
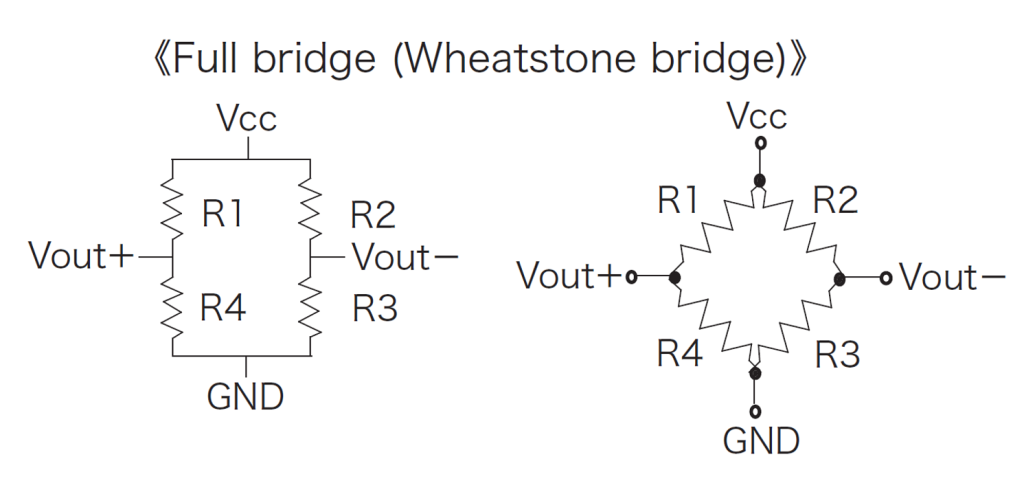
It represents the resistance value per bridge (between Vcc and GND: in the case of a 2-phase bridge, when both ends are connected in parallel) or per element in no magnetic field.
It represents the voltage output from Vout (Vout+, Vout-) when 5V is applied between Vcc-GND in no magnetic field.
It represents the difference between the midpoint potential of Vout+ and Vout− when 5V is applied between Vcc-GND in no magnetic field.
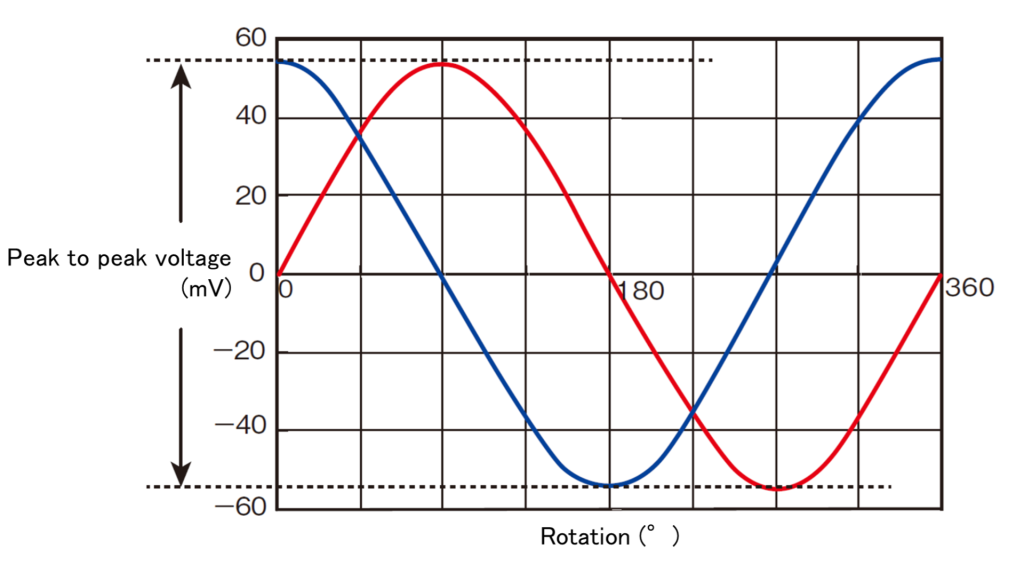
It represents the amount of change in midpoint potential in a magnetic field under certain conditions.
At our company, the applied voltage is based on 5V. The output voltage is proportional to the applied voltage.
Represents the width of the amplitude of the output voltage. When a rotating magnetic field is applied to an AMR sensor for position detection/rotation detection, it will be twice the output voltage in the case of a half-bridge, and four times the output voltage in the case of a full-bridge.
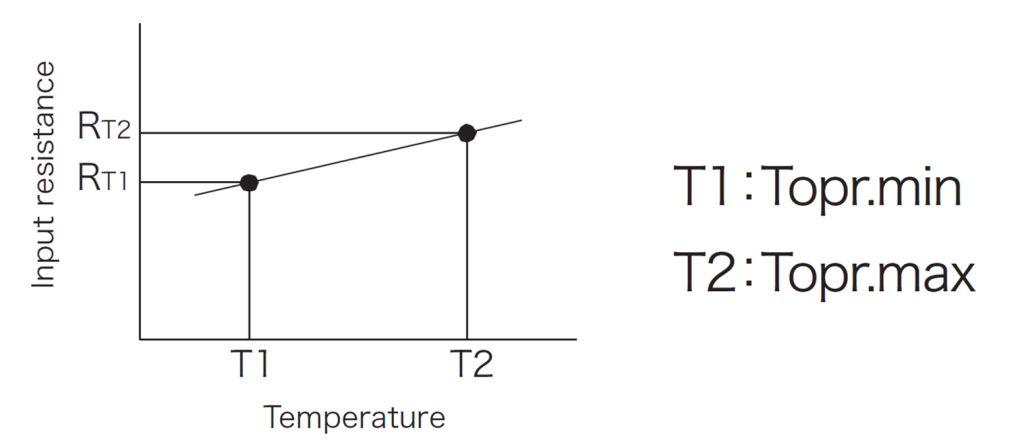
(RT2 – RT1) ∕ {RT1 (T2 – T1)} x 100 (%/°C)
RT1: Resistance value (Ω) at T1 (°C)
RT2: Resistance value (Ω) at T2 (°C)
We use the following two types of notation depending on the difference in notation method.
9-1.
Midpoint potential temperature drift
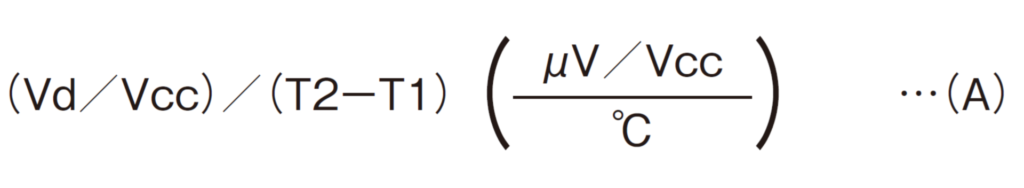
Vd:Drift amount(μV) at Vcc(V)
9-2.
Midpoint potential temperature drift
Drift amount when Vcc = 5V and the operating ambient temperature of each product is substituted for T1 and T2 in formula (A)
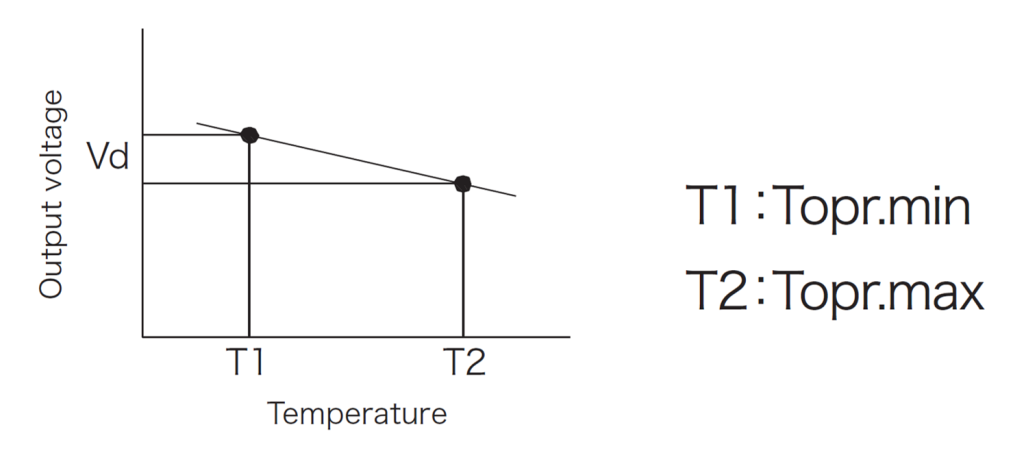
(V T2 – V T1) / {V T1 (T2 – T1)} x 100 (%/°C)
V T1: Output voltage (V) at T1 (°C)
V T2: Output voltage (V) at T2 (°C)
Magnetic field (H) 1kA/m = 12.5 Oe
Since the magnetic permeability (μ) is about 1 in the atmosphere,
From B = μH, the relationship with the magnetic flux density (B) is 1 Oe ≒ 0.1mT.
It represents the distance from the center of the N pole to the center of the S pole in a magnet magnetized with multiple poles.